Learning Styles
Everyone learns differently. Psychologist Neil Fleming suggests that most children and adults tend to fall into four basic learning styles:
- Visual: Visual Learners process and understand information through pictures, diagrams, and other visual stimuli. For example, they may remember things by designing a flow chart.
- Auditory: Auditory Learners process and understand information through spoken words. They may remember things by adding a rhythm or beat to them.
- Reading/Writing: Reading/Writing Learners process and understand information through the written word or by writing themselves. These learners will be the students fervently taking notes or highlighting text in a book.
- Kinesthetic: Kinesthetic Learners process and understand information through movement and demonstration. They remember through doing. Demonstrate a task and then allow them to do the task themselves. These are hands-on learners.
Traditional Schools Do Not Cater to All Learning Styles
Traditional schools accommodate auditory learning styles well through lectures and reading/writing style learners through textbooks and written assignments. However, kinesthetic and very visual learners are often left floundering.
Emerging virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools promise better education for visual and kinesthetic learners. Using these tools:
- Visual Learners can observe objects at all angles and watch processes in action, such as cell division or photosynthesis.
- Kinesthetic learners can encounter a supportive environment that addresses their need to learn by moving and doing.
The Benefits of VR and AR for Visual Learners
Visual learners prefer to see information rather than hear it or read it. They can benefit from VR and AR tools that allow them to:
- Explore 3-D models of objects, such as planets, molecules, or human anatomy.
- Interact with simulations of natural phenomena. For instance, watching a tornado form with color-coded weather patterns. Can they predict whether a tornado will form? Will it touch down?
- Visualize abstract mathematical concepts, such as algebra, geometry, or statistics.
- Create digital art, designs, or animations to explain a theory, hypothesis, or idea.
The Benefits of VR and AR for Kinesthetic Learners
According to a 2019 blog from MIT’s Media Lab, “Due to its immersive nature and body-tracking capabilities, VR can allow learners to do kinesthetic activities in an environment that is able to track and understand their movements, provide real-time feedback, and engage them in activities within novel contexts that strongly relate to their physical actions.” Kinesthetic learners prefer to learn by doing rather than watching or listening. They can benefit from VR and AR tools that allow them to:
- Perform hands-on experiments in a virtual lab.
- Manipulate physical objects with haptic feedback.
- Use their physical skills in virtual sports, music, or learning a trade.
- Engage in immersive games or scenarios that allow them to learn by doing.
Examples of VR and AR in Education
To give you some inspiration, here are some examples of how VR and AR are being used in education:
- History and Geography: Students can travel back in time and visit historical sites, such as ancient Rome, the Pyramids, or the Colosseum. They can experience an immersive exploration of different cultures and places, such as China, India, or Antarctica. They can also interact with historical figures, such as John F Kennedy, Martin Luther King Jr., or Gandhi, and learn about their lives and achievements.
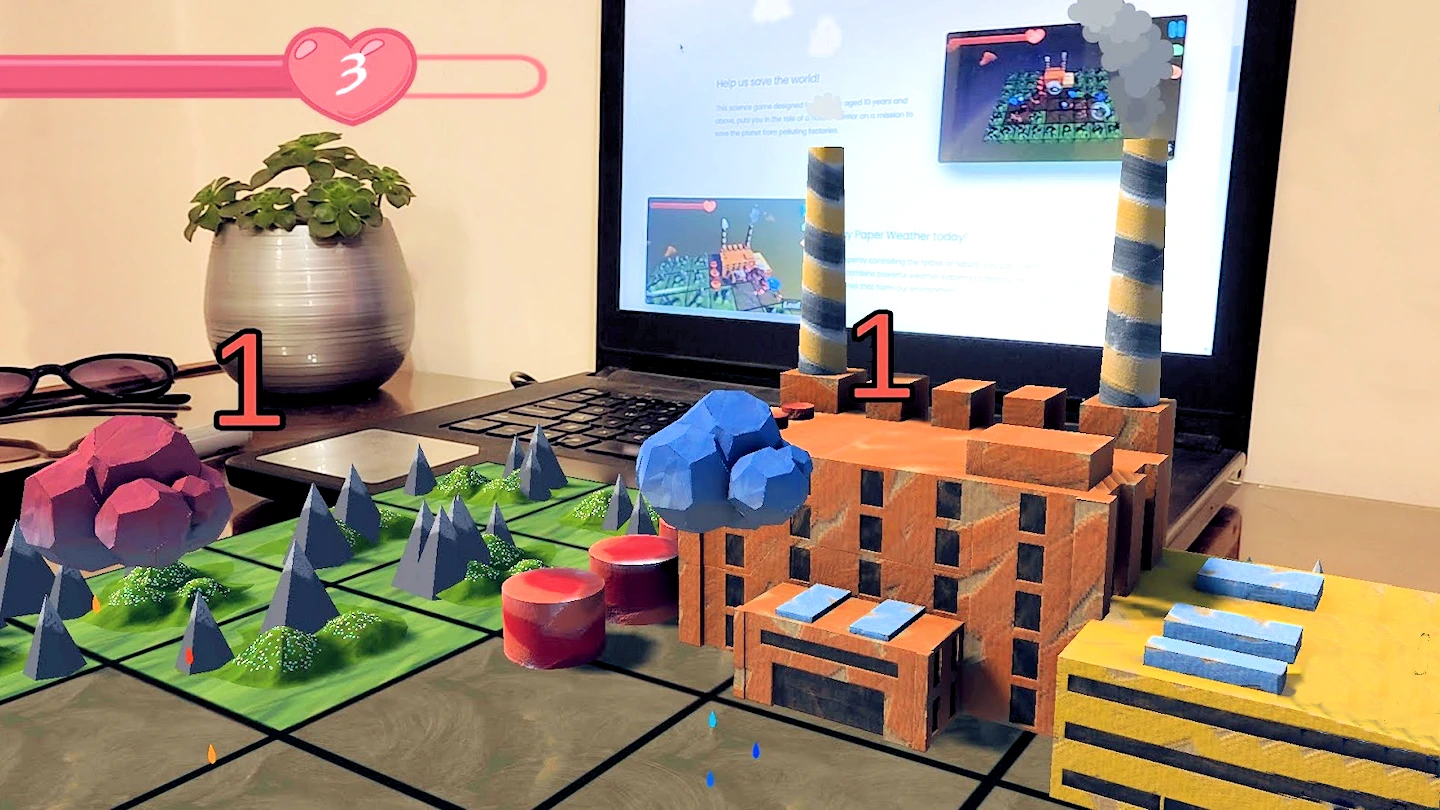
- Science and Math: Students can conduct experiments and observe phenomena that are difficult or impossible to replicate in a real classroom. They can visualize chemical reactions, gravity, or electricity. Mathematical concepts can be manipulated and visualized and we can see how they relate to real-world problems.
- Art and Music: Students can create their art and music using VR and AR tools, such as Tilt Brush or GarageBand. They can also learn from famous artists and musicians, such as Van Gogh, Picasso, or Mozart, and see their works and techniques in 3-D.
- Language and Literature: Students can practice their language skills by immersing themselves in a virtual environment where they can speak and listen to native speakers. They can also experience literary works in a new way by entering the worlds of their favorite books and characters, such as Harry Potter, Alice in Wonderland, or The Lion King.
The Future of VR and AR in Education
Some students can read instructions, listen to a lecture, and take notes all day but never really master a task until they can physically do it themselves. Lab experiments and physical tools for teaching young children attempt to address this need, but VR and AR can take it to the next level.VR and AR have the potential to revolutionize education by catering to different learning styles and providing personalized and engaging experiences for students. As these technologies become more accessible and affordable, we can expect to see more applications of VR and AR in classrooms and beyond.
Summary
The integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into education offers promising solutions for addressing diverse learning styles, particularly for visual and kinesthetic learners who often struggle in traditional classroom settings. By enabling immersive experiences—such as exploring 3-D models, conducting virtual experiments, and engaging with historical events—these technologies create dynamic learning environments that enhance comprehension and retention. As VR and AR continue to evolve and become more accessible, they hold the potential to transform educational practices, fostering personalized learning experiences that cater to individual needs and ultimately enriching the educational landscape for all students.