In today’s digital age, games have transcended their traditional role as mere sources of entertainment. They’ve morphed into potent educational tools, especially in the areas of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM Education). As we navigate through the 21st century, we must acknowledge how games mold tomorrow’s future scientists, engineers, and innovators.
Why Games Matter in STEAM Education
- Engagement and Immersion: Games are designed to captivate. Their interactive nature ensures that players are not just passive recipients but active participants. Engaging in an immersive learning experience can make complex subjects like physics or coding easily understandable and more enjoyable.
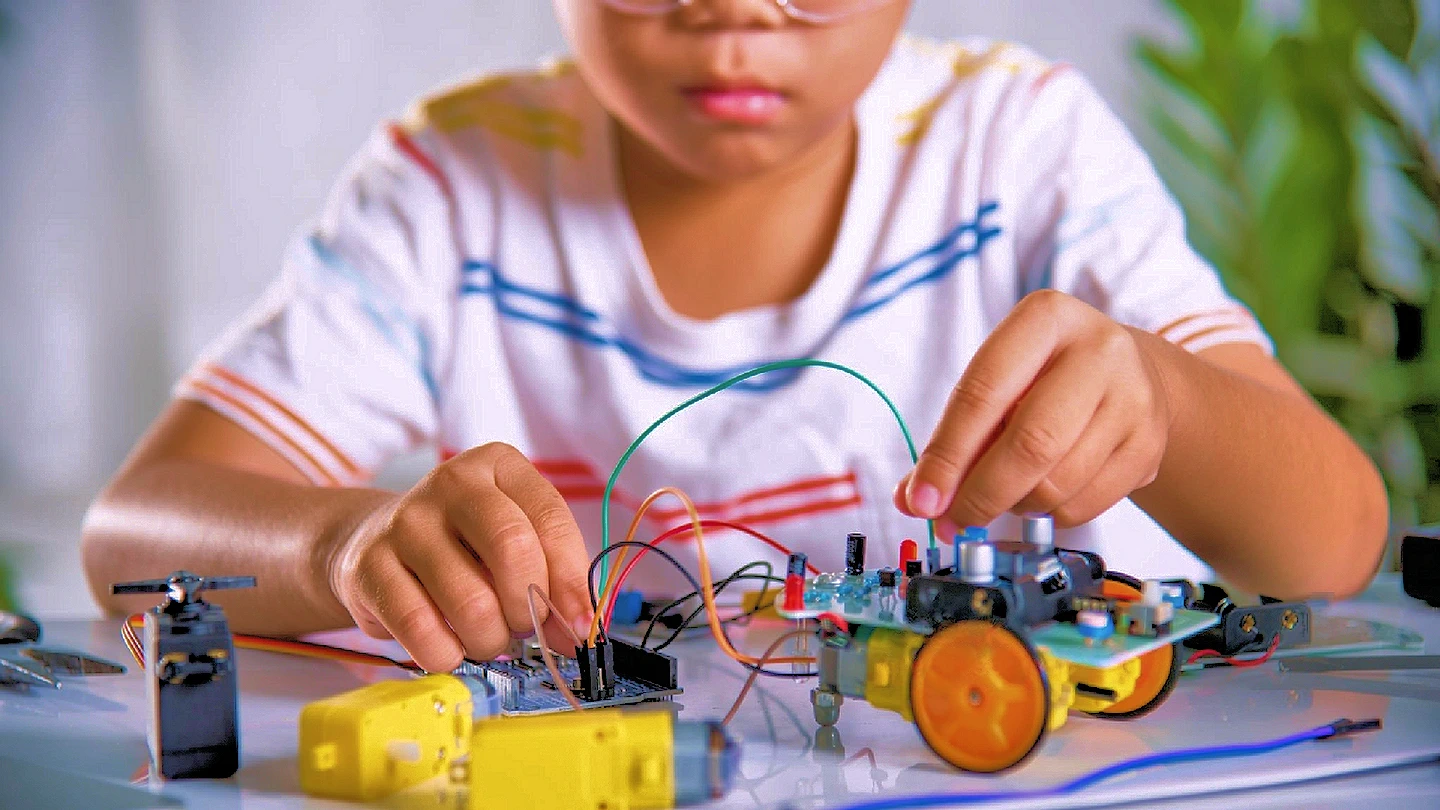
- Problem-Solving Skills: Most games are a series of challenges or puzzles at their core. To advance, players must think critically, strategize, and apply knowledge. These cognitive exercises mirror the problem-solving skills essential in STEAM fields. For example, a game in which a player’s task is to build bridges using a finite amount of resources can introduce basic engineering concepts.
- Creativity and Innovation: Sandbox games like Minecraft or Roblox empower kids to construct their worlds, fostering a sense of creativity and innovation. These platforms not only entertain but also offer insights into architectural design, engineering principles, and even the rudiments of computer programming. Platforms like Scratch and Code.org gradually introduce kids to the programming world through game design, instilling a sense of confidence and capability and a feeling of empowerment in their learning journey.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Games that contain multiplayer features often require players to collaborate, and they teach the essence of teamwork. The majority of traditional STEAM projects are collaborative endeavors, making these gaming experiences invaluable.
Real-world Applications: Games in the Classroom
The educational sector is paradigm-shifting, with many educators integrating games into their curricula. Platforms like Alter-Learning champion this fusion of traditional education and game-based learning.
Here’s a deeper dive into the classroom applications:
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Labs: Traditional textbooks can make certain scientific concepts seem abstract. Using VR and AR, students can immerse themselves in a virtual lab, witness chemical reactions, or explore the human anatomy in 3D. This hands-on approach can clarify complex ideas.
- Math Games: Beyond the overtly educational games, even mainstream games involve mathematical concepts. Whether it’s scoring, resource management, or spatial reasoning, players inadvertently hone their math skills.
- Coding Bootcamps: Platforms like Scratch and Code.org introduce kids to the programming world through game design. These platforms demystify coding by allowing students to create games, transforming them from a daunting subject into a fun activity.
How Do Games Help Students Develop Problem-Solving Skills?
Games are designed to be a series of challenges or puzzles at their core. To advance, players must think critically, strategize, and apply knowledge. These cognitive exercises mirror the problem-solving skills essential in STEAM fields. As students overcome these challenges, they experience a sense of accomplishment, which is a powerful motivator for learning. Games can introduce basic engineering concepts, physics, coding, and more complex subjects, making them more accessible and enjoyable.
Parental Perspective: More than Just Playtime
For many parents, screen time can be a contentious issue. However, it’s essential to distinguish between mindless scrolling and educational gaming. When utilized correctly, games can become formidable educational allies.
Parents play a crucial role in instilling a love for STEAM subjects.
- Understanding and Responsibility: Parents can foster a deeper understanding and sense of responsibility regarding technology use by guiding their children toward educational games or discussing the science and logic behind their favorite games. This involvement not only enhances the educational value of gaming but also strengthens the parent-child bond.
- Differentiating Gaming Types: Parents can encourage kids to choose games that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity while setting limits on screen time to mitigate mindless scrolling on social media.
The Road Ahead: Preparing for the Future
As our world undergoes rapid technological evolution, the importance of STEAM education intensifies. Games uniquely blend entertainment and education, equipping children for a future where technology is ubiquitous. They serve not just as pastimes but as vital tools for cultivating the next generation of scientists, engineers, artists, and mathematicians.
Summary
Games are increasingly integral to STEAM learning, merging fun with valuable educational experiences in problem-solving, teamwork, creativity, and real-world applications. Embracing this trend in schools and communities is essential to prepare future generations for an ever-complex world. By championing educational gaming, we can ensure that tomorrow’s innovators are equipped with the skills they need to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the overall effect of digital game-based STEAM education on students’ learning achievement?
The overall effect of digital game-based STEAM education on students’ learning achievement is generally favorable. Research indicates that integrating digital games into STEAM education can enhance student motivation, engagement, and retention of the material.
Games provide interactive, immersive, and problem-solving experiences that can make abstract STEAM concepts more tangible and relatable. When designed effectively, they can tailor the learning experience to individual student’s pace and preferences, allowing for personalized learning.
Are the learning gains higher when using digital games to support STEAM education as compared to non-digital game-based methods?
Learning gains from using digital games to support STEAM education can sometimes be higher than non-digital game-based methods. The advantages of digital games include adaptability, immediate feedback, and the ability to simulate complex systems or phenomena that may be difficult to replicate in traditional settings.
However, the efficacy of learning also heavily depends on the quality of the game design, how it’s integrated into the curriculum, and the specific learning objectives being targeted. Some traditional or non-digital methods can be equally or more effective in certain contexts or for specific learning outcomes.
Does the subject discipline impact students’ learning achievement in digital game-based learning settings?
Yes, the subject discipline can impact students’ learning achievement in digital game-based learning settings. Some STEAM subjects might lend themselves more readily to game-based simulations or scenarios.
For instance, physics or mathematics concepts might be easily integrated into game mechanics, while certain biological processes might require more abstract representation.
Additionally, students’ prior knowledge and interest in the discipline can also affect how effectively they learn through digital games.
Does the educational level influence students’ learning achievement in digital game-based learning settings?
The educational level does influence students’ learning achievement in digital game-based settings. Younger students, for instance, might benefit more from games that focus on basic concepts and have a more straightforward design. Games can become more complex as students advance, integrating multiple concepts and requiring higher-order thinking skills.
However, it’s essential to ensure that the game’s difficulty and content are appropriate for the student’s educational level to prevent frustration or disengagement.
Do the gameplay designs (game types or gaming platforms) affect student achievement in digital game-based learning settings?
Absolutely. The design of gameplay, including the game type (e.g., puzzle, strategy, simulation) and the gaming platform (e.g., PC, mobile, virtual reality), can significantly influence student achievement. Some game designs might better suit specific learning outcomes or cater to specific learning styles.
For instance, a simulation game might best teach system dynamics, while a puzzle game might be more appropriate for problem-solving tasks. The platform also impacts accessibility, user experience, and the level of immersion, all of which can influence learning outcomes.
Does the intervention duration impact students’ learning achievement in digital game-based learning settings?
Yes, the duration of the intervention can affect students’ learning achievement. Short-term game interventions might boost engagement and provide immediate reinforcement of certain concepts.
However, extended gameplay or multiple gaming sessions spread over time might be necessary for deeper understanding and long-term retention. Like any educational tool, the effectiveness of game-based learning often depends on its thoughtful and consistent integration into the broader curriculum.